OrganRegen-Estradiol(C502820)
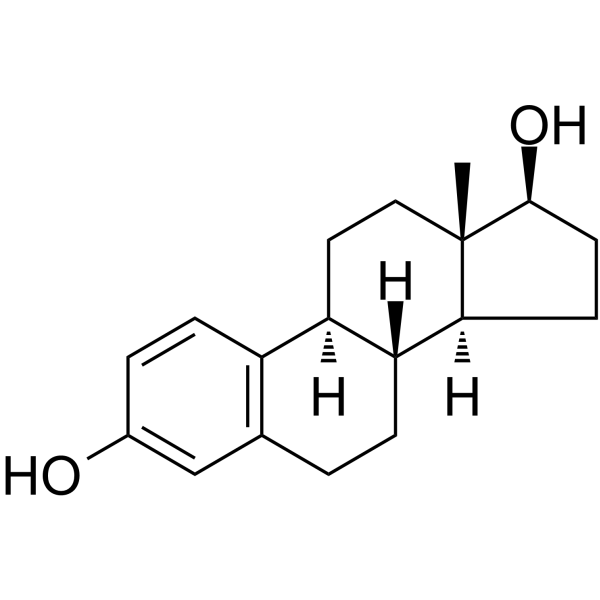
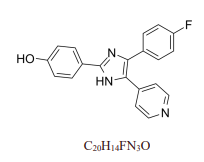
Estradiol
貨號:C502820
規(guī)格:1g
品牌:OrganRegen
產(chǎn)品介紹
DESCRIPTION
Background | Estradiol is a steroid sex hormone vital to the maintenance of fertility and secondary sexual characteristics in females. Estradiol upregulates IL-6 expression through the estrogen receptor β (ERβ) pathway[1][2][3]. |
技術(shù)參數(shù)
Alias | β-Estradiol; E2; 17β-Estradiol; 17β-Oestradiol雌二醇;強力求偶素 | ||
M. W t | 272.38 | ||
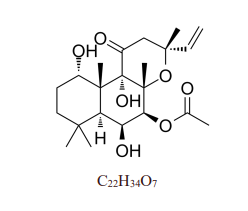
Formula | C18H24O2 | ||
CAS No | 50-28-2 | ||
Storage | Powder | -20°C | 3 years |
4°C | 2 years | ||
In solvent | -80°C | 6 months | |
-20°C | 1 month | ||
Solubility | DMSO | ≥ 100 mg/mL(283.71 mM) | |
Ethanol | 14 mg/mL(51.40 mM) | ||
H2O | < 0.1 mg/mL(insoluble) | ||
BIOLOGICAL ALTIVITY
Estradiol causes new dendritic spines and synapses in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells. Estradiol increases NMDA receptor binding by 46% in parallel with dendritic spine and synapse density. Estradiol also elevates sensitivity of CA1 pyramidal cells to NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic input and such an effect is correlated with the estradiol-induced increase in dendritic spine density in the apical dendritic tree of these cells[1]. Estradiol reduces Ba2+ entry reversibly via Ca2+ channels in acutely dissociated and cultured neostriatal neurons. Estradiol also reduces Ba2+ currents but is significantly less effective than Estradiol in rat neostriatal neurons[2].
In Vivo
Estradiol functions in hippocampal synapse density during the estrous cycle in the adult rat[4].Estradiol reverses the ovariectomy-induced decrease in spine density. Estradiol in combination with progesterone enhances spine density for 2 to 6 h but decreases following estradiol alone[5].Estradiol (0.2 mg/kg; i.p.; C57BL/6 female mice) plus 10 or 20 mg/kg progesterone, enhances memory consolidation in young ovariectomized mice[6].
REFERENCES